The future of distribution on Android and iOS has arrived
With a single, seamless integration Catappult now offers the best of two worlds on Android and iOS: direct-to-consumer (D2C) distribution and monetisation, and distribution in over 10 app stores across the world. Always with the best revenue split on the market.
Brought to you by

Leverage your Games distribution in iOS + Android
Aptoide is the first app store to offer mobile developers a combined solution for distribution and monetisation in both Android and iOS

Your trusted Merchant of Record
As your Merchant of Record, Catappult handles the calculation, filing and payment of all software sales tax based on your customers’ specific locations, guaranteeing compliance with regional tax laws.
This means that you can focus on developing and marketing your apps and games without the added stress of managing complex tax laws and transaction fees. Our goal is to streamline your operations, ensuring that your tax and fee management is effortless and worry-free, so you can fully zero in on what you do best.
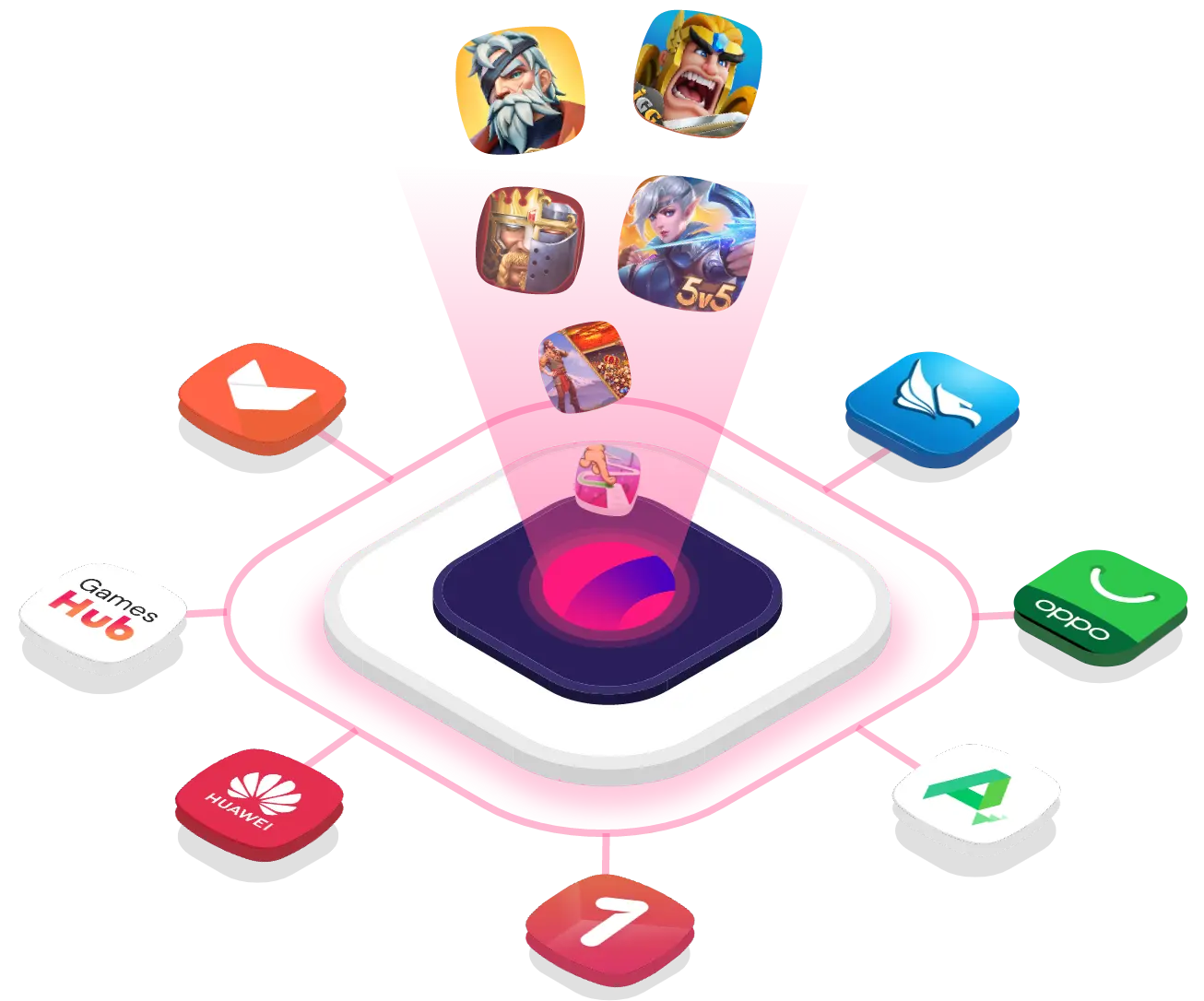
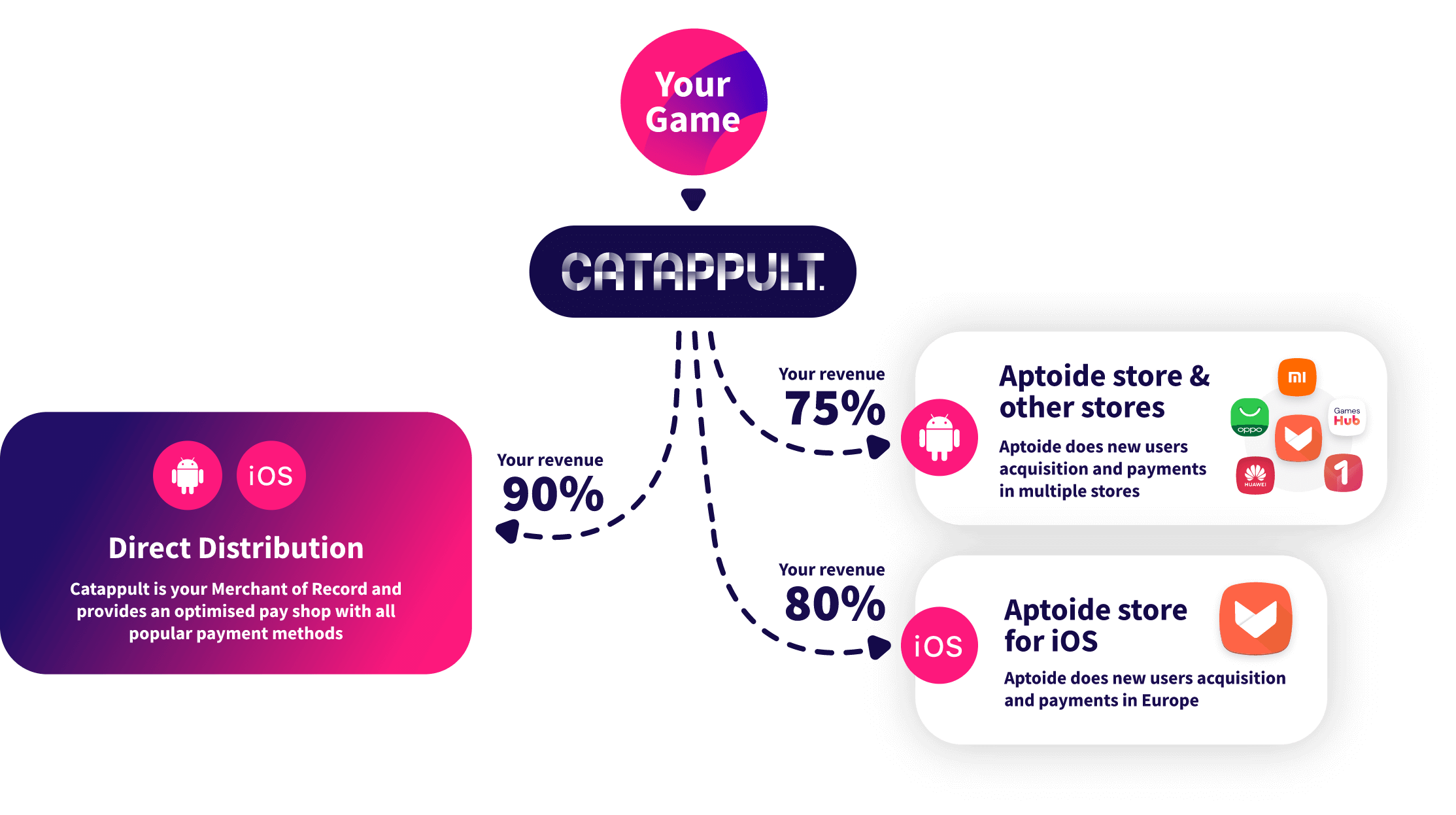
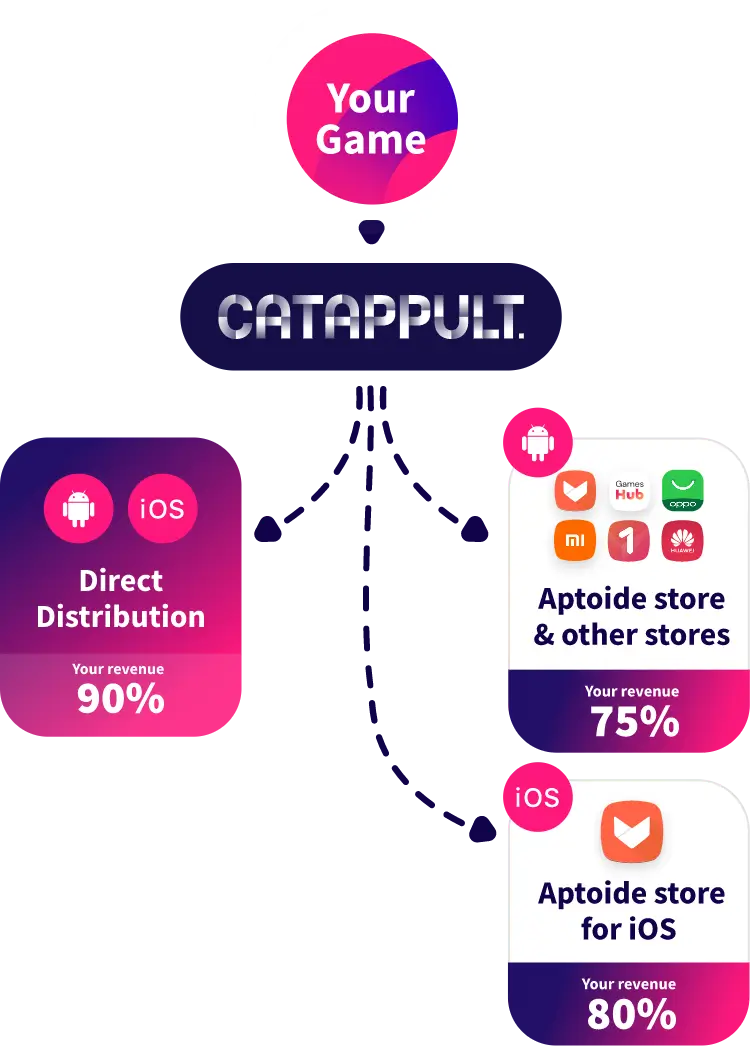
Go directly to consumers on Android and iOS
Catappult’s new direct-to-consumer distribution model for Android and iOS gives developers an exceptionally profitable 90% revenue split, completely free of any hidden charges.
In addition, we offer an unbeatable 75% revenue share model on earnings from our partners' app stores. This makes Catappult's universal platform for both Android and iOS by far the best solution for developers to swiftly grow their international presence and immediately capitalize on that expansion.


Distribute to 10+ app stores on Android and iOS
With Catappult you immediately get your game or app on 10+ app stores on Android and iOS reaching over 430 million users.
With our new combined distribution on Android and iOS, Catappult really is the one-stop shop for mobile developers to effortlessly connect with multiple app stores and other global channels. If you want seamless universal multiplatform distribution, Catappult is the only way to go.
The easiest billing solution
Our One Step Payment (OSP) is the ultimate convenient solution to implement Catappult billing.
Our OSP system operates through a straightforward HTTP request. When a customer is ready to make a purchase, OSP initiates a secure connection that launches the AppCoins Wallet application. This specialized app is the cornerstone of the payment process, ensuring a secure and efficient transaction. Once the AppCoins Wallet is activated, the customer can effortlessly complete their payment. The OSP system then receives a prompt notification of the transaction outcome. Based on the result, it will confirm whether the item or service can be released to the customer.

The iOS ecosystem is changing and soon we will be supporting alternative stores for iOS apps distribution. Do you want to distribute your game or app to iOS stores?

Developers that joined us






























Case Studies
on Catappult

on Catappult

on Catappult

Our Partner App Stores
Check the app stores and OEMs that can distribute your apps!











From the blog